Cockpit
Siehe auch
Webmin
Cockpit Version 195.12. Das Versionierungsschema ist an das von Systemd angelehnt.
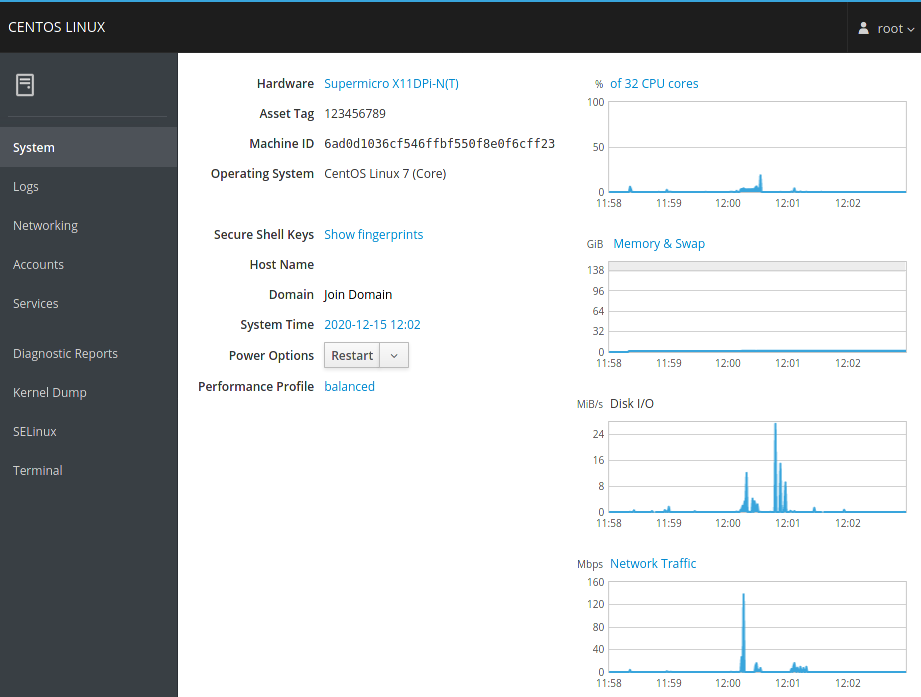
Das bei Red Hat entwickelte Cockpit ist ein einfaches, web-basiertes „Linux Server Admin Interface“, mit dessen Hilfe sich ein RHEL oder eine kleine Server-Farm bequem im Browser verwalten und monitoren lässt. Cockpit kommt auch mit virtuellen Maschinen und der Docker-Alternative Podman zurecht.
Es arbeitet ausschliesslich mit Systemd, und ist daher auch auf Ubuntu 17+ und Debian 9+ einsetzbar. Zudem benötigt es so im Vergleich zu anderen Produkten keine weiteren Bibliotheken.
- Links:
Source Code: https://github.com/cockpit-project/cockpit
Die Installation ist schnell erledigt:
dnf -y install cockpit
systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Eingehend Port 9090/tcp freigeben:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=cockpit
firewall-cmd --reload
Die Web-Konsole lässt sich über diverse Plugins erweitern, die teils aus dritten Projekt-Repos bezogen werden können:
dnf -y install cockpit-389-ds
dnf -y install cockpit-composer # Building custom OS images
dnf -y install cockpit-file-sharing
dnf -y install cockpit-kdump
dnf -y install cockpit-machines # Managing libvirt virtual machines
dnf -y install cockpit-navigator
dnf -y install cockpit-networkmanager
dnf -y install cockpit-ostree
dnf -y install cockpit-ovirt-dashboard # from oVirt repo
dnf -y install cockpit-packagekit # Managing packages, and installing updates and applications
dnf -y install cockpit-podman # Managing podman containers
dnf -y install cockpit-selinux
dnf -y install cockpit-sosreport
dnf -y install cockpit-storaged # Managing system storage
Zugriff erfolgt auf https://cockpit:9090. Eigene TLS-Zertifikate werden in /etc/cockpit/ws‐certs.d/ abgelegt.
Performance-Metriken:
dnf -y install cockpit-pcp # Collecting performance metrics
systemctl restart pmlogger
Um Session-Recording einzurichten:
dnf -y install cockpit-session-recording
systemctl enable --now sssd
Um auf der Konsole einzelne Sessions aufzunehmen und wieder abzuspielen:
tlog-rec --file-path=tlog.log
# do your work
tlog-play --file-path=tlog.log
Built on 2025-10-27